
Simple Heatmap in R with Formula One Dataset Rbloggers
Saving your heatmaply into a file. Create an interactive html file: dir.create ( "folder" ) heatmaply (mtcars, file = "folder/heatmaply_plot.html" ) browseURL ( "folder/heatmaply_plot.html") Saving a static file (png/jpeg/pdf). Before the first time using this code you may need to first run: webshot::install_phantomjs () or to install plotly.
How to make a heatmap in R Ryan Johnson
This is the most basic heatmap you can build with R and ggplot2, using the geom_tile () function. Input data must be a long format where each row provides an observation. At least 3 variables are needed per observation: x: position on the X axis. y: position on the Y axis. fill: the numeric value that will be translated in a color.
Heatmap In R Static And Interactive Visualization Datanovia ZOHAL
The heatmap function has the form of heatmap(x, scale, na.rm, col, labRow, labCol, main) and it produces a heat map of the data. x is the numeric matrix containing the values being used in creating the heat map. col is the color palette to be used by the heat map. na.rm is a logical value that determines whether NA values should be removed.
Heatmap in R Static and Interactive Visualization Datanovia
How to plot a heatmap and its legend, i.e. a bar with the color scale representing the minimum and the maximum value that are plotted? I read the help of the heatmap() function, and using base R as explained here: r-graph-gallery.com heatmaps. this is what I'm doing

Making a heatmap with R Dave Tang's blog
Version 1.1.9. Date 2021-01-05. Author Shilin Zhao, Linlin Yin, Yan Guo, Quanhu Sheng, Yu Shyr. Maintainer Shilin Zhao
Heatmap in R Static and Interactive Visualization Datanovia
R base heatmap: heatmap() The built-in R heatmap() function [in stats package] can be used. A simplified format is: heatmap(x, scale = "row") x: a numeric matrix; scale: a character indicating if the values should be centered and scaled in either the row direction or the column direction, or none. Allowed values are in c("row", "column.
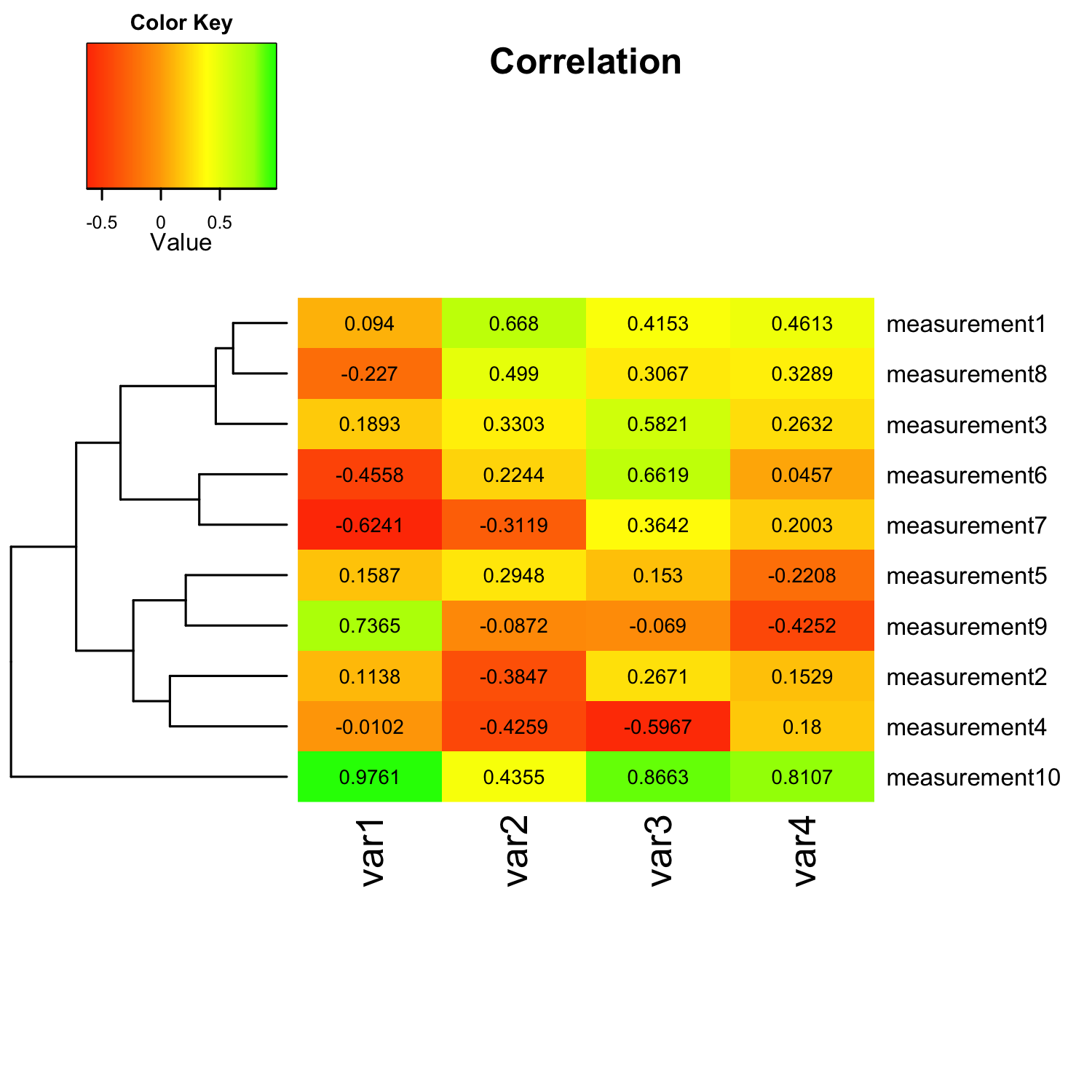
A short tutorial for decent heat maps in R
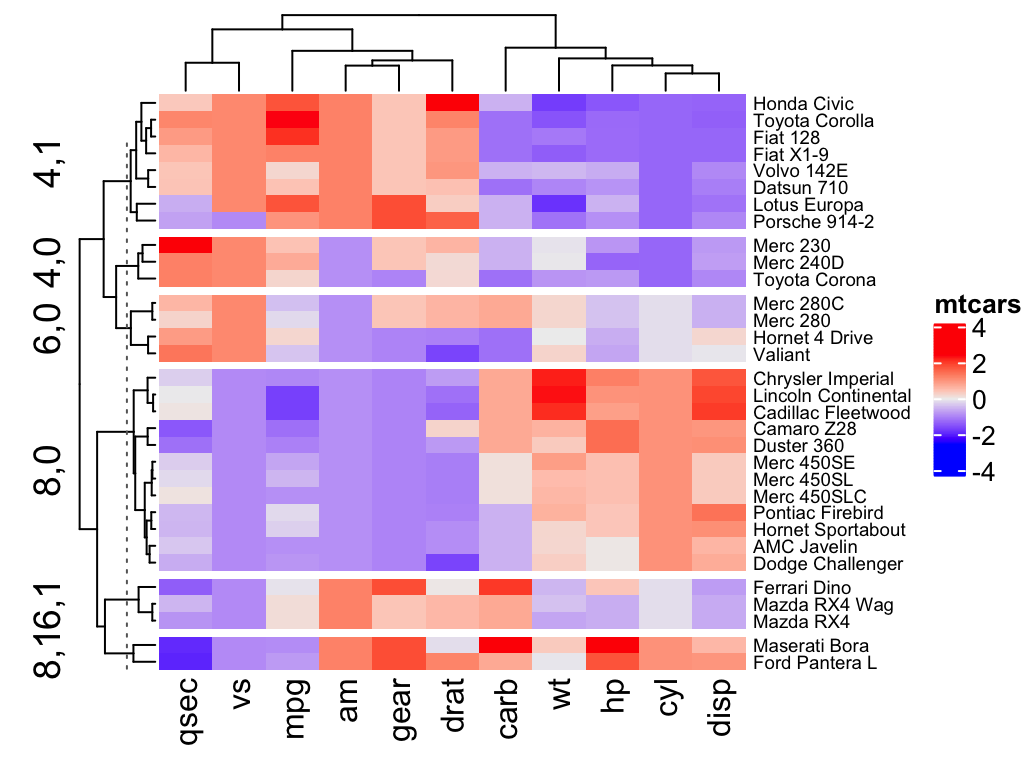
However, the two heatmaps (scaled by rows and columns, respectively) look very different. Note, I've removed the dendrograms and sorted the names alphabetically for easy comparison. scale = "row". scale = "column". The white sections of the plots correspond to a given species whose comparison to all other species results in δ δ = 1.

R Continuous gradient color & fixed scale heatmap ggplot2 iTecNote
A heat map is a false color image (basically image (t (x))) with a dendrogram added to the left side and/or to the top. Typically, reordering of the rows and columns according to some set of values (row or column means) within the restrictions imposed by the dendrogram is carried out. This heatmap provides a number of extensions to the standard.
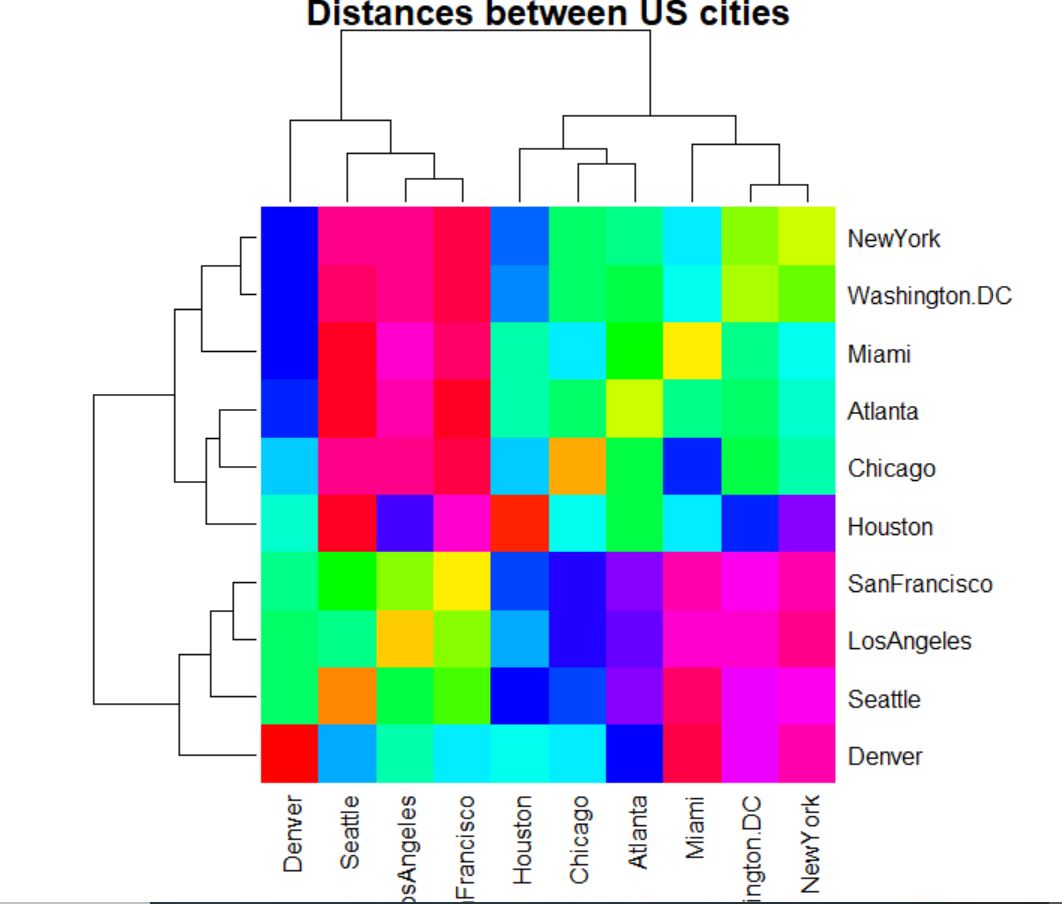
How To Make a Heatmap in R (With Examples) ProgrammingR
V a l u e s = V a l u e s − M e a n S t a n d a r d. D e v i a t i o n. An alternative to standardization is the mean normalization, which resulting distribution will have between -1 and 1 with mean = 0. Mean normalization formula: Transformed. Values = Values − Mean Maximum − Minimum T r a n s f o r m e d.
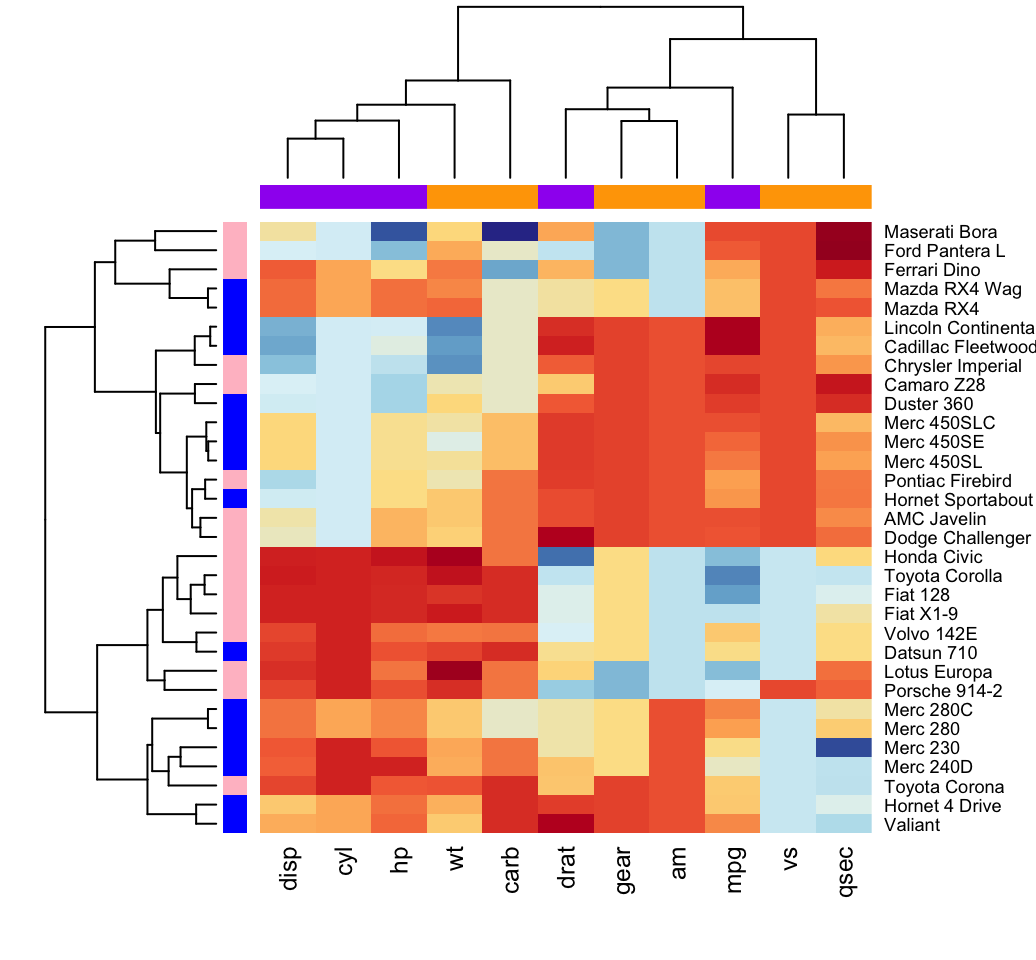
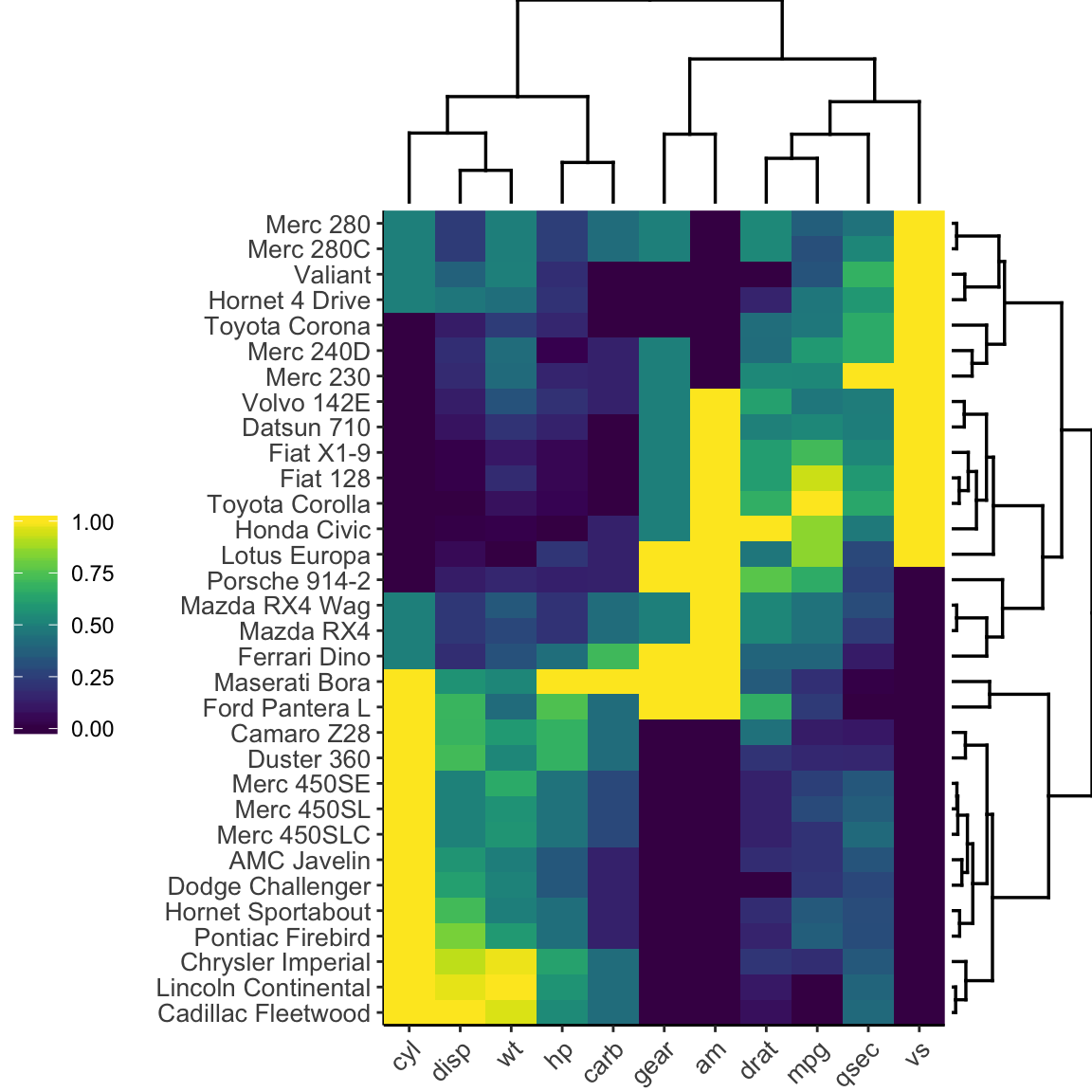
Heatmap in R Static and Interactive Visualization Datanovia
Description. A heat map is a false color image (basically image (t (x))) with a dendrogram added to the left side and to the top. Typically, reordering of the rows and columns according to some set of values (row or column means) within the restrictions imposed by the dendrogram is carried out.
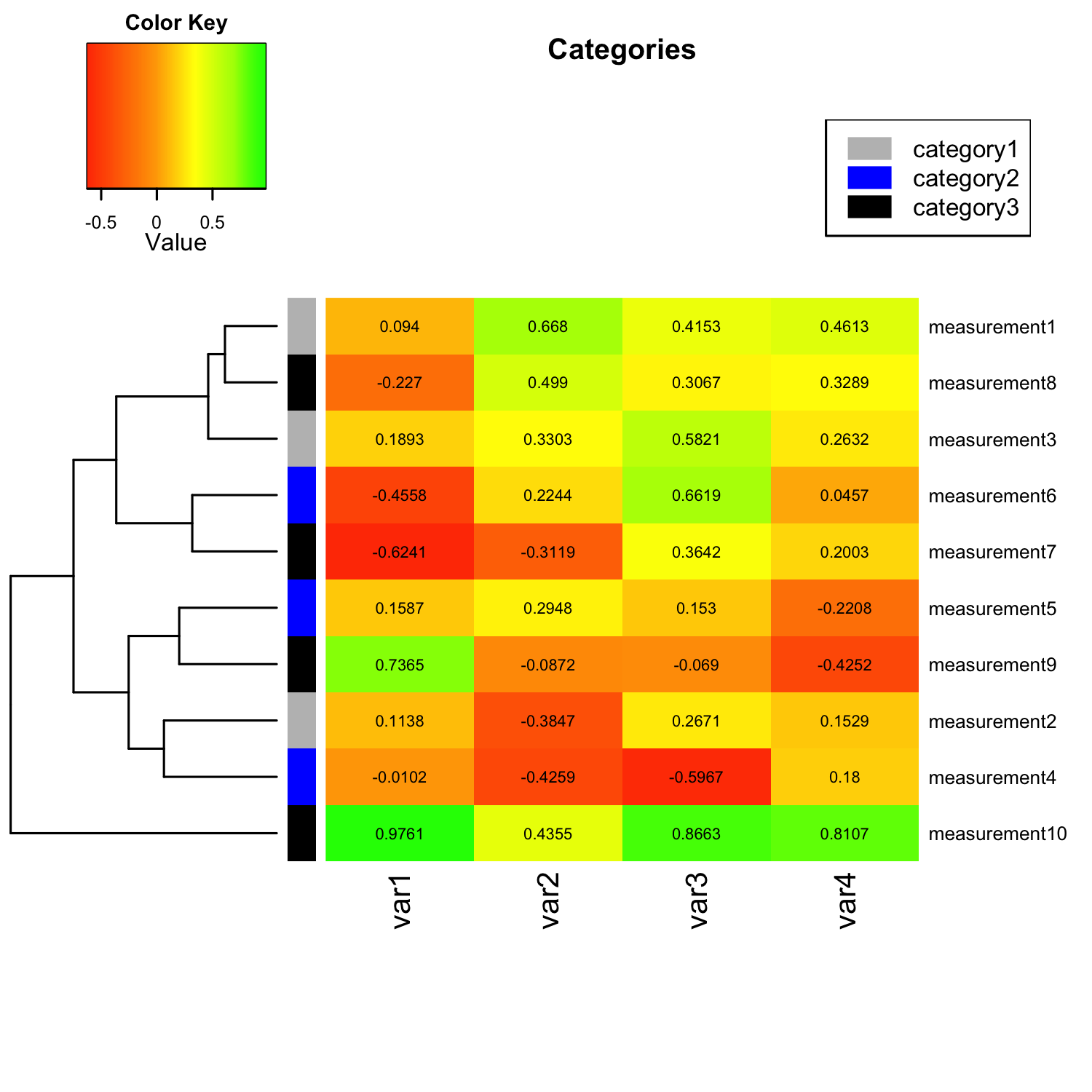
A short tutorial for decent heat maps in R
For the first question, to add color scale bar, there are several methods using other packages. First way is using gplot::heatmap.2. gplots::heatmap.2 (dummy, scale = "none", col = bluered (100), trace = "none", density.info = "none") Second way is using pheatmap::pheatmap. It will plot clustered heatmap.
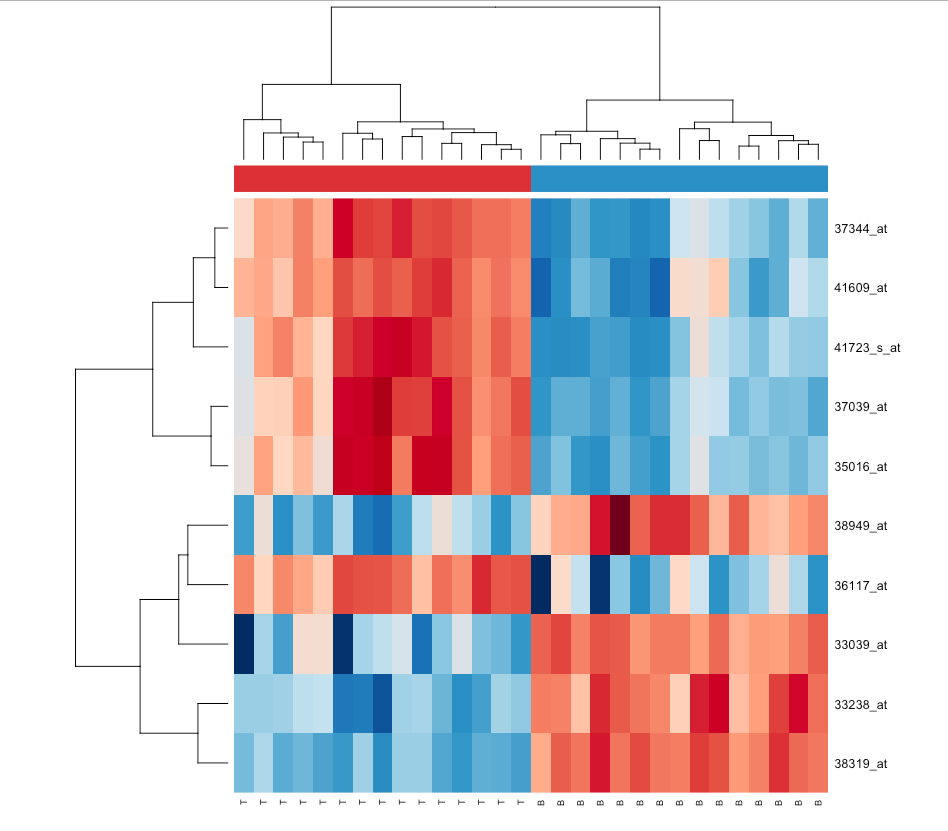
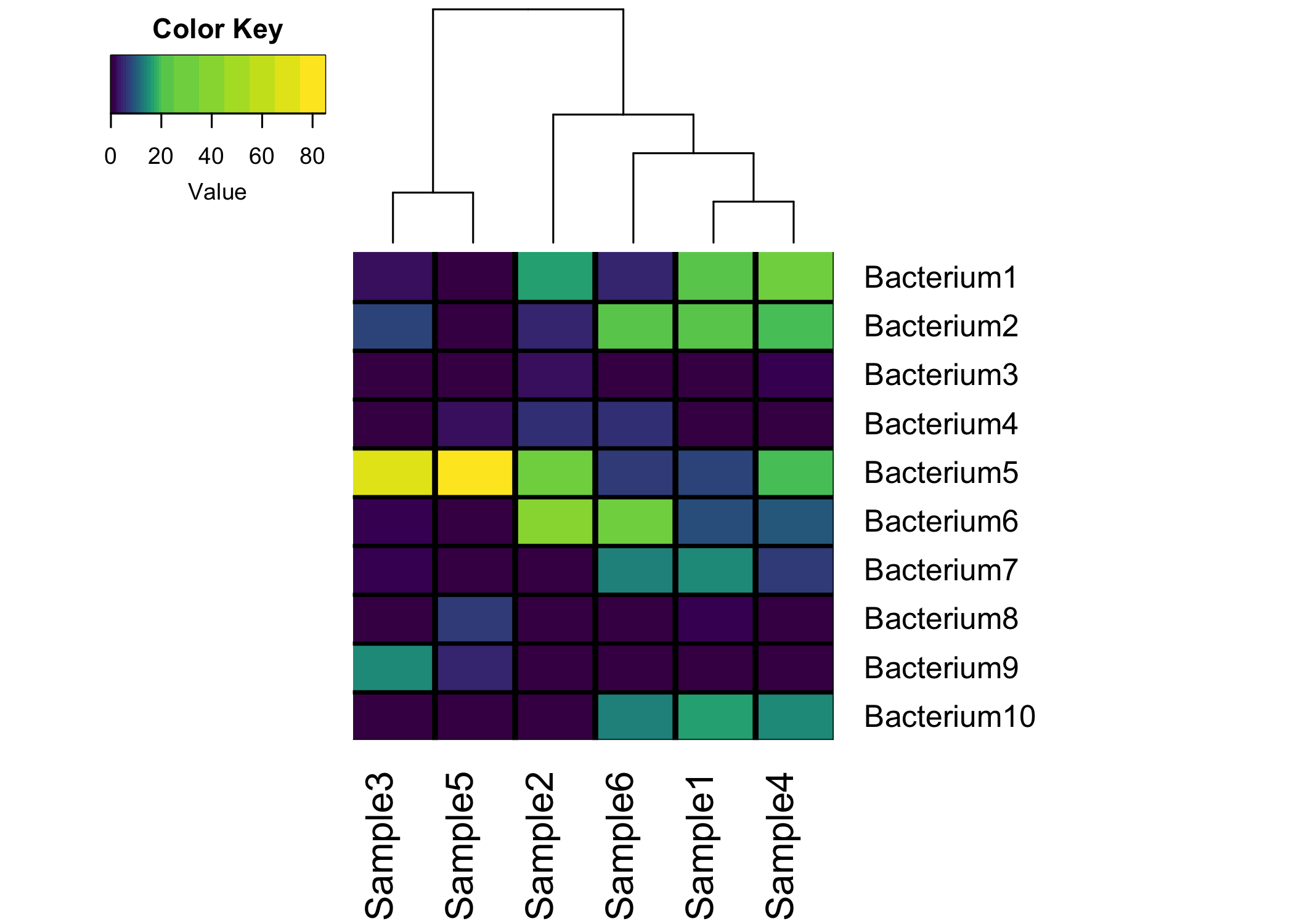
R Heatmap Open Source Biology & Interest Group
We can also change up the colors of the heatmap by changing the colors used in the scale_fill_gradient () argument: #create heatmap using blue color scale ggplot (melt_mtcars, aes (variable, car)) + geom_tile (aes (fill = rescale), colour = "white") + scale_fill_gradient (low = "white", high = "steelblue")
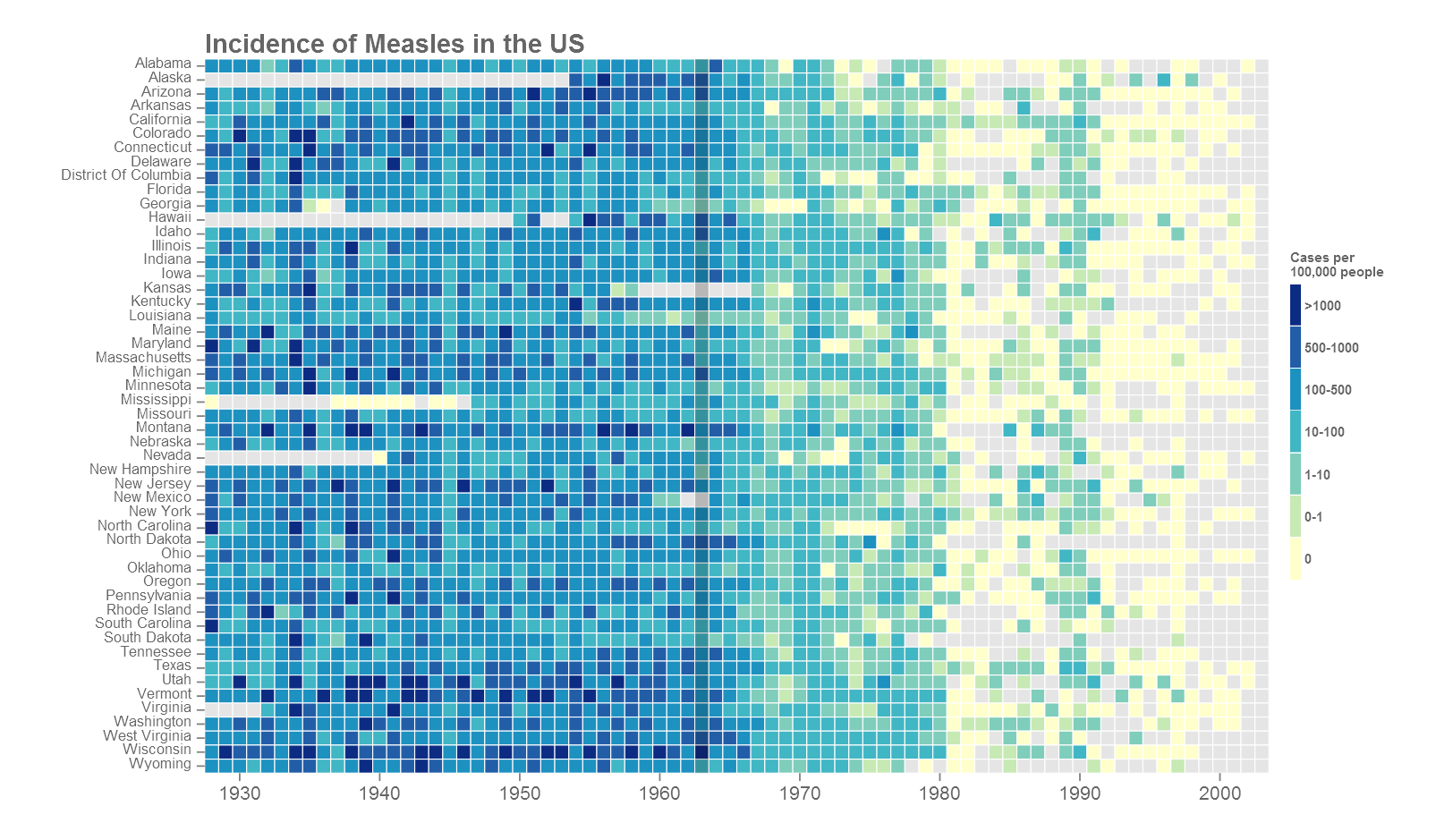
A guide to elegant tiled heatmaps in R [2019] • rmf
Most basic Heatmap. How to do it: below is the most basic heatmap you can build in base R, using the heatmap () function with no parameters. Note that it takes as input a matrix. If you have a data frame, you can convert it to a matrix with as.matrix (), but you need numeric variables only. How to read it: each column is a variable.
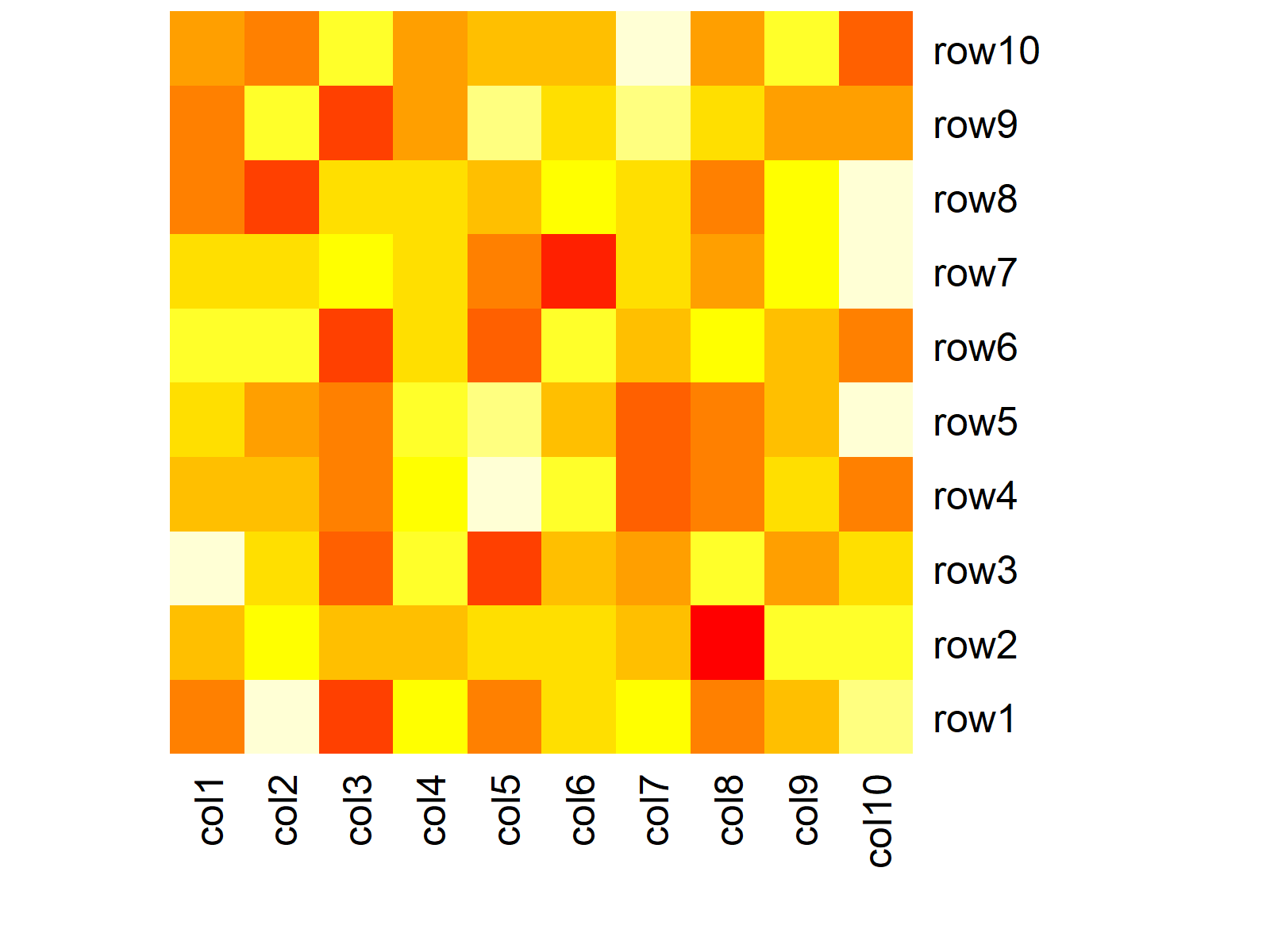
Create Heatmap in R (3 Examples) Base R, ggplot2 & plotly Package
This article describes how to create clustered and annotated heatmaps for visualization of gene expression data obtained from RNA-seq experiments using a pheatmap R package. Install pheatmap. If you have not installed pheatmap package, you can install it using install.packages () Load pheatmap library. You need to load the pheatmap library for.

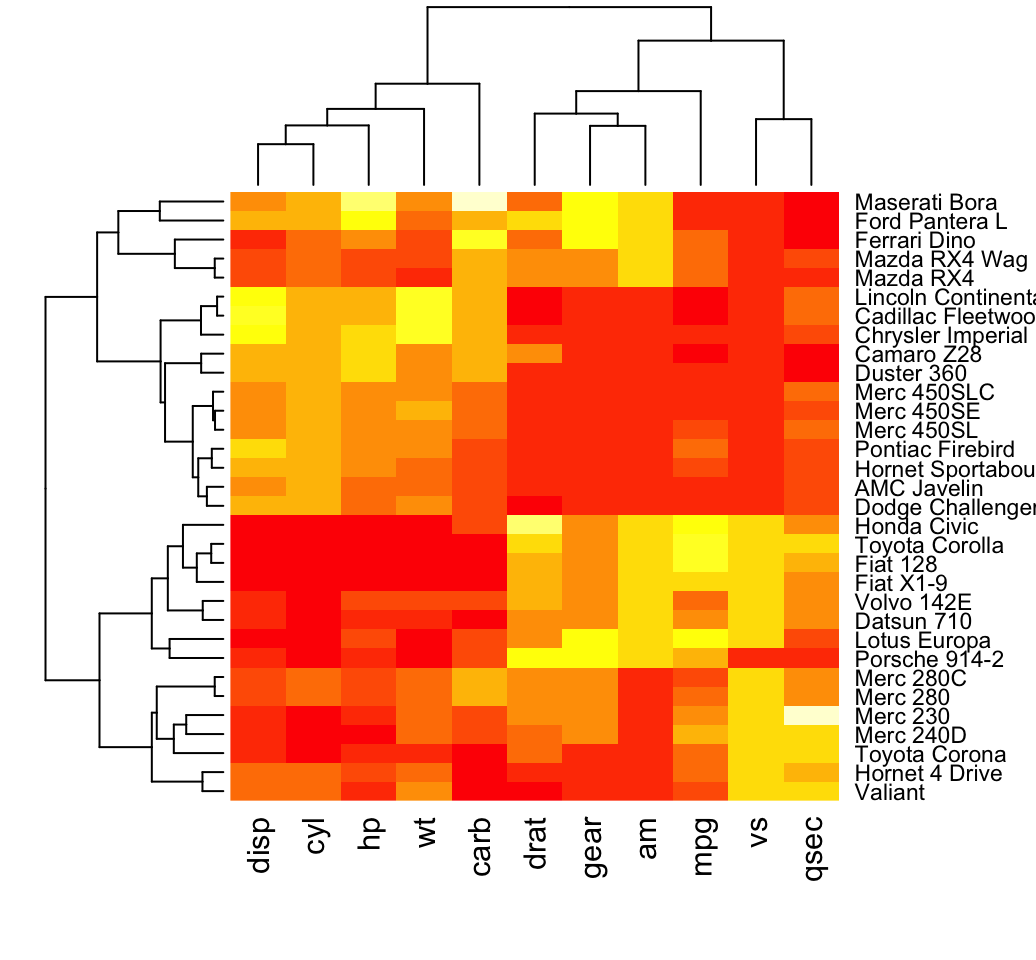
Building heatmap with R the R Graph Gallery
function used to compute the distance (dissimilarity) between and rows. Will be the same as distfun if not specified. balanceColor. logical indicating if the colors need to be balanced so that the median color will represent the 0 value. The default value is F. ColSideLabs. label for ColSideColors. RowSideLabs.
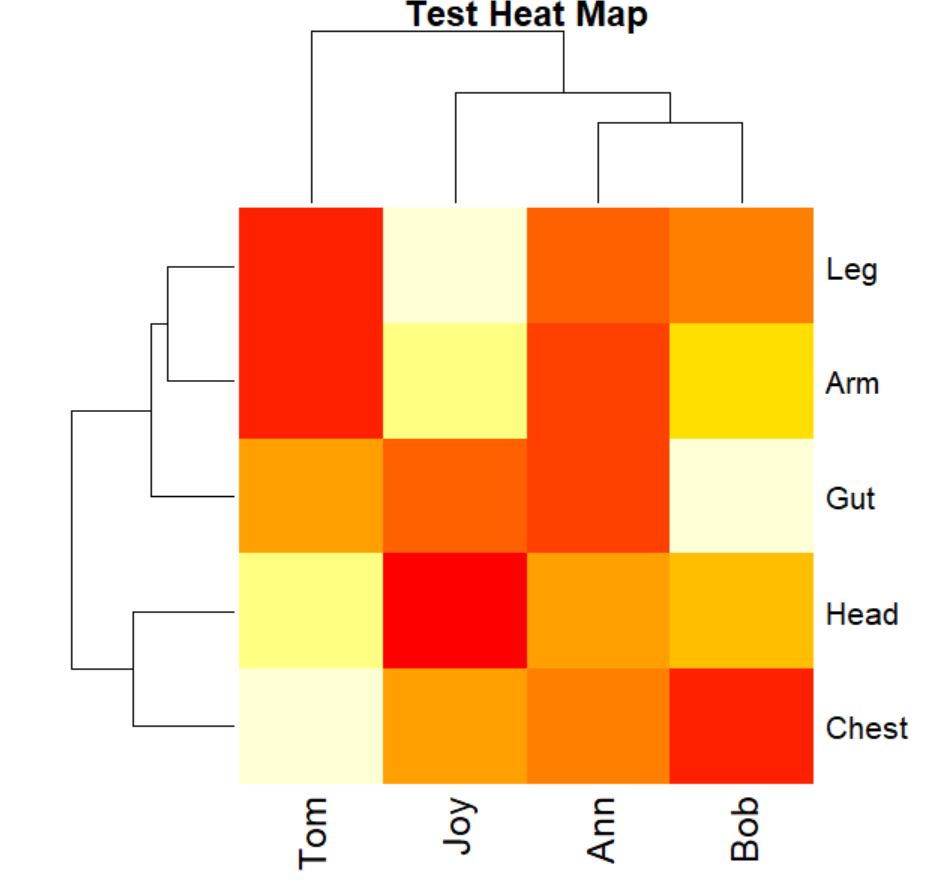
How To Make a Heatmap in R (With Examples) ProgrammingR
Thanks Sven Hohenstein -- The color scale will span across the data range, so with same redgreen(50) it will be same red or green for data ranging from -1 to +1 and for data ranging from -.2 to +.2. but the reason to let the color span across [-1,1] on data ranging [-.2, .2] is to be able to visualize the difference in data.